How to Improve Your Attic Ventilation For Your Roof

Ever wonder if your attic space is helping your home or hurting it? Believe it or not, proper attic ventilation is a big deal—not just for your roof but for your entire home’s health. Unfortunately, many homeowners don’t give it much thought until problems start popping up.
At Roof MD, we know a well-ventilated attic isn’t just a “nice to have”—it’s a must. Good airflow keeps your attic free of trapped heat and moisture, saves you money on energy bills, and helps your roof last longer. Let’s dive into why taking care of your attic’s air circulation is one of the smartest investments you can make.
Why Roof Attic Ventilation Is a Game Changer
Think of your attic as your home’s lungs. Without proper airflow, it can turn into a hot, humid trap, which leads to all kinds of headaches. Here’s what can go wrong if your attic isn’t ventilated properly:
- Your Roof Ages Faster: Hot air trapped in your attic during summer can literally cook your shingles from the inside, causing them to warp, crack, and wear out way too soon. Good ventilation helps keep your attic cooler and protects your roof from damage.
- Mold and Moisture Take Over: Everyday activities like cooking and showering create moisture that rises into the attic. If there’s no airflow, that moisture can settle on cooler surfaces, leading to mold, mildew, and even rot. No one wants that!
- Skyrocketing Energy Bills: An overheated attic makes your AC work overtime to keep your home cool. In the winter, poor ventilation can also cause heat to escape, driving up your energy costs even more. Proper ventilation keeps your home’s temperature stable all year.
- Ice Dams (If You Live in a Cold Climate): Bad ventilation can cause warm air to melt snow on your roof, which then refreezes at the edges, forming ice dams. These can cause leaks and water damage—definitely not fun to deal with.
- Bad Indoor Air Quality: Mold spores and stale attic air can creep into your living spaces, triggering allergies and making it harder to breathe. Good attic ventilation helps keep your home’s air fresher and healthier.
By optimizing your attic ventilation system, you’ll avoid these headaches and enjoy a more comfortable, energy-efficient home. Ready to breathe a little easier? Let’s get started!
Understanding How Roofing Ventilation Works
Let’s talk about attic ventilation—it’s all about balance. A good system needs both intake and exhaust vents to keep the air flowing properly:
- Intake Vents: These are usually found in the soffits (under your roof’s overhang) or near the lower part of the roof. They pull in fresh air from outside.
- Exhaust Vents: Located at or near the roof’s peak (think ridge vents, turbine vents, or box vents), these let warm, moist air escape.
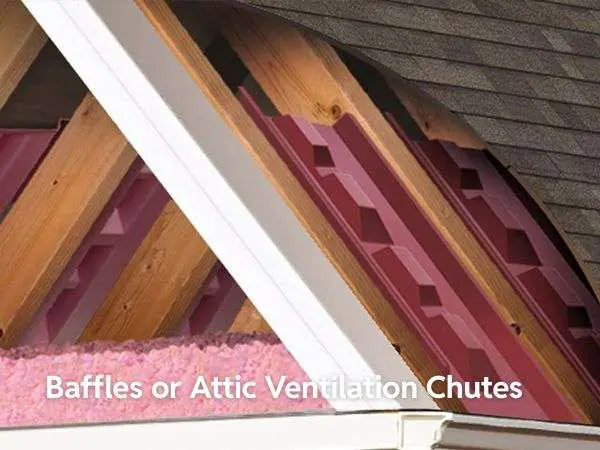
- Baffles or Attic Ventilation Chutes: Baffles are essential for proper attic ventilation, ensuring airflow from intake vents isn’t blocked by insulation. Placed between the roof decking and attic insulation, they direct air smoothly from the soffit to the attic. Proper installation prevents issues like winter ice dams, reduces moisture, and helps extend your roof’s lifespan by keeping attic temperatures stable year-round.
This airflow happens naturally, with hot air rising and cooler air coming in to replace it. Sometimes, wind helps out too. The goal? Consistent air circulation to flush out heat and moisture, keeping your attic in great shape.


Signs Your Attic Ventilation Needs Help
Wondering if your attic ventilation isn’t cutting it? Keep an eye out for these signs:
- Your Upper Floors Are Hotter: If your upstairs feels like a sauna compared to downstairs, your attic might be trapping too much heat.
- Mold or Mildew in the Attic: Spotting mold on the underside of your roof or on insulation? That’s a moisture problem tied to poor airflow.
- Wet or Damp Insulation: Insulation that’s soggy or compressed isn’t doing its job and is a clue that moisture is building up in the attic.
- Peeling Paint or Rusty Nails: Too much moisture can make paint peel or cause nails to rust.
- Ice Dams in Winter: Those icicles hanging off your roof? They’re pretty but are a classic sign of poor ventilation and insulation.
- High Energy Bills: If your heating or cooling costs seem unusually high, poor attic airflow might be a factor.
- Warped Shingles: Heat buildup in the attic can actually damage your shingles, causing them to warp or crack.
How to Fix and Improve Your Attic Ventilation
Think your attic ventilation could use some work? Don’t worry—we’ve got solutions:
- Make Sure You Have Enough Ventilation: Building codes spell out how much ventilation your attic needs based on its size. A pro can help calculate if you’re meeting the standard.
- Balance Intake and Exhaust: It’s not just about having vents; they need to be balanced—half for intake, half for exhaust.
- Clear the Roof Vents: Check that insulation, debris, or stored items aren’t blocking airflow.
- Choose the Right Attic Vent Types: Depending on your roof and climate, you might need:
-
- Ridge Vents for continuous airflow along the roof peak.
- Soffit Vents under the eaves for intake.
- Turbine Vents (Whirlybirds) that use wind to pull out air.
- Box Vents that passively release heat and moisture.
- Power Attic Ventilators (PAVs) like electric or solar fans to actively move air (use these with care and sensors like thermostats).
-
- Check Insulation: Proper insulation works with ventilation to regulate attic temperature, but make sure insulation isn’t blocking soffit vents. Use baffles if needed.
- Seal Air Leaks: Prevent warm, moist air from your home from sneaking into the attic by sealing leaks.
Why Roof MD Can Help

Attic ventilation isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s essential for keeping your home in good shape and running efficiently. At Roof MD, we get it. Our team can inspect your ventilation, point out any issues, and recommend the best fixes to protect your roof and make your home more comfortable.
Don’t let poor airflow cause problems down the line. Contact Roof MD today, and let’s make sure your home is protected from the top down!