Flat Roofing 101: Pros & Cons, Repairs & More!
Looking for a new roof or need help with your flat roof? You’re in the right place. This blog covers everything you need to know about flat roofing: what it is, types, pros and cons, and common repairs. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of your flat roof and how to handle any issues.
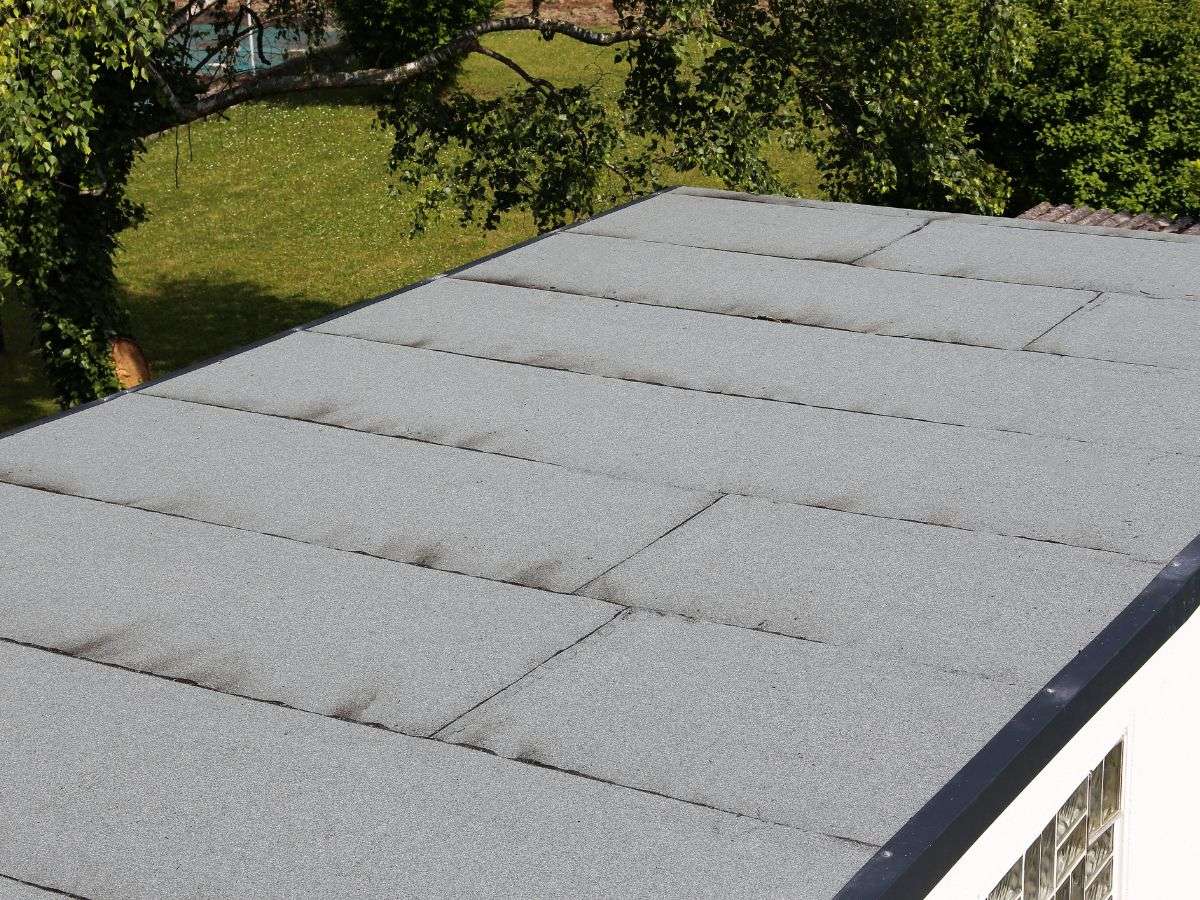

What is Flat Roofing?
Flat roofing may sound straightforward, but there’s more to it. While flat roofs appear level, they’re usually slightly pitched (5 to 15 degrees) to help water drain properly. In this guide, we’ll cover the basics, including types, materials, and benefits.
Pros of Flat Roofing:
Easy maintenance & access:
Flat roofs are easier and safer to maintain than sloped roofs, making debris removal and inspections simple. This allows for efficient repairs and upkeep with less injury risk.
Additional space:
Flat roofs offer extra usable space for storage or mounting equipment like HVAC units. Some even use them as recreational areas, like rooftop gardens or patios.
Reflective surfaces:
Flat roofs often use reflective materials to lower cooling costs by reducing heat absorption, making them eco-friendly and energy-efficient.
Aesthetics:
Flat roofs can complement modern design, won’t block scenic views, and can feature “green” elements like rooftop gardens that improve air quality and insulation.
Cons of Flat Roofing:
Leaks:
Flat roofs are more prone to leaks due to limited drainage. Regular inspections and timely repairs are needed to avoid damage. Water can travel under the roof before appearing, making leaks harder to locate.
Snow and ice:
Flat roofs can accumulate snow and ice, leading to weight strain, ice dams, and leaks. Regular removal and solutions like heating cables are essential to prevent damage.
Heat loss:
Flat roofs can lose heat quickly, making them less energy-efficient in colder months. Proper insulation and routine checks can help reduce heating costs and improve comfort.
Types of Flat Roofing:
Flat roofing materials come in several options, each with its own pros and cons. Below is a breakdown to help you decide based on cost, durability, maintenance, and weather resistance.
Built-Up Roof (BUR)
BUR is a flat roofing system made of bitumen and fabric layers for a durable, waterproof surface.
Pros:
- BUR systems are long-lasting and fire-resistant. With proper maintenance, they can last over 20 years, offering robust protection. Regular inspections help maximize their lifespan, making them cost-effective.
Cons:
- Poor installation can cause ponding water and damage, so professional installation is a must.
- Gravel re-coating is required every 1-2 years, depending on sun and weather exposure, to maintain protection.
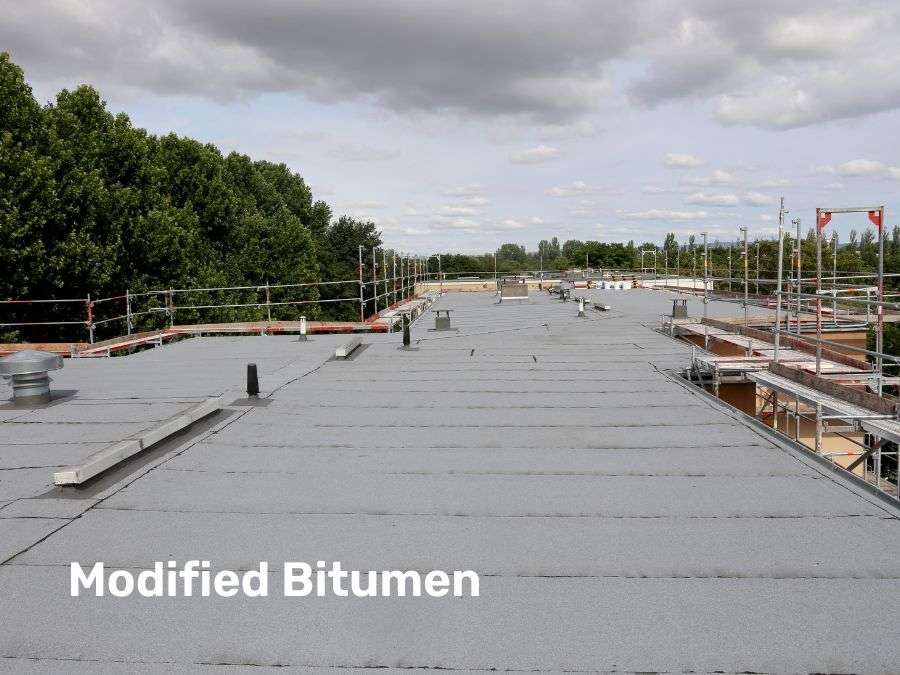
Modified Bitumen
Modified Bitumen mixes asphalt with polymers like SBS (Styrene Butadiene Styrene) or APP (Atactic Polypropylene).
Pros:
- It can be applied using cold adhesives, hot mopping, or torch-down methods. These options provide flexibility, with cold adhesives being safe and easy.
- With regular checks and maintenance, these roofs can last 10-20 years, protecting the structure below.
Cons:
- More expensive than BUR systems, but many consider the added durability worth the cost.
- Installation is complex and may require skilled labor and specialized tools, increasing costs.


EPDM
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) is a synthetic rubber, commonly black but also available in grey.
Pros:
- Affordable and easy to install, making it a budget-friendly option without sacrificing quality.
Cons:
- Prone to punctures if not installed and maintained properly, so experienced professionals are key.
- May not suit all climates or building types, so comparing options is important.
TPO/PVC
Thermoplastic Polyolefin (TPO) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are modern materials for residential flat roofs. TPO sheets are seamed, while PVC seams are welded.
Pros:
- Fire-resistant and durable, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Energy-efficient, offering long-term savings despite a higher upfront cost.
Cons:
- TPO can be more expensive than other options and requires proper installation to avoid punctures and leaks. Regular maintenance ensures performance and longevity.
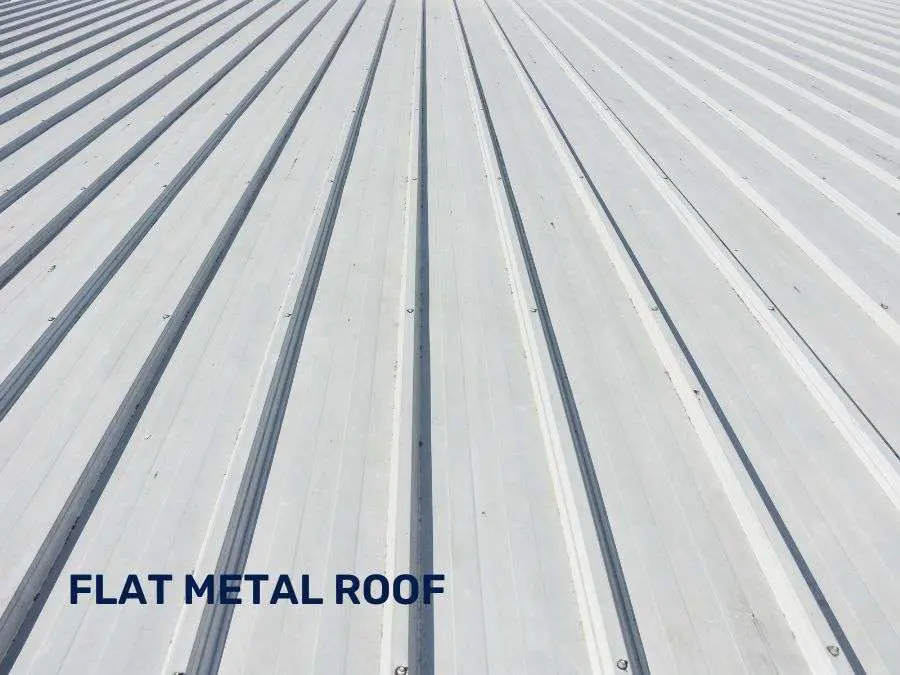


Metal Roofs
Metal roofs work on flat or low-slope roofs and come in materials like copper, zinc, steel, and aluminum.
Pros:
- Extremely durable, lasting up to 50 years or more with proper care.
- Excellent protection against extreme weather, such as hail, heavy rain, and snow.
Cons:
- Higher upfront costs compared to other flat roofing materials, but their long lifespan offsets this over time.
- Regular maintenance is needed to prevent rust and corrosion, with cleaning and minor repairs extending their life.
Flat Roof Cost
The cost of a flat roof depends on factors like materials, size, complexity, and labor. Flat roofing materials generally cost more upfront than traditional sloped roofs.
However, flat roofs can save money in the long run with their durability, low maintenance, and longer lifespan, meaning fewer replacements.
The average installation cost ranges from $5-$10 per square foot, depending on the material. Here’s a cost breakdown:
- PVC: $6-$10 per square foot
- TPO: $5-$8 per square foot
- EPDM: $4.50-$6.50 per square foot
- Built-up Roof (BUR): $3.50-$6 per square foot
Keep in mind that costs can vary based on roof size, complexity, location, and labor.
Common Repairs for Flat Roofing:
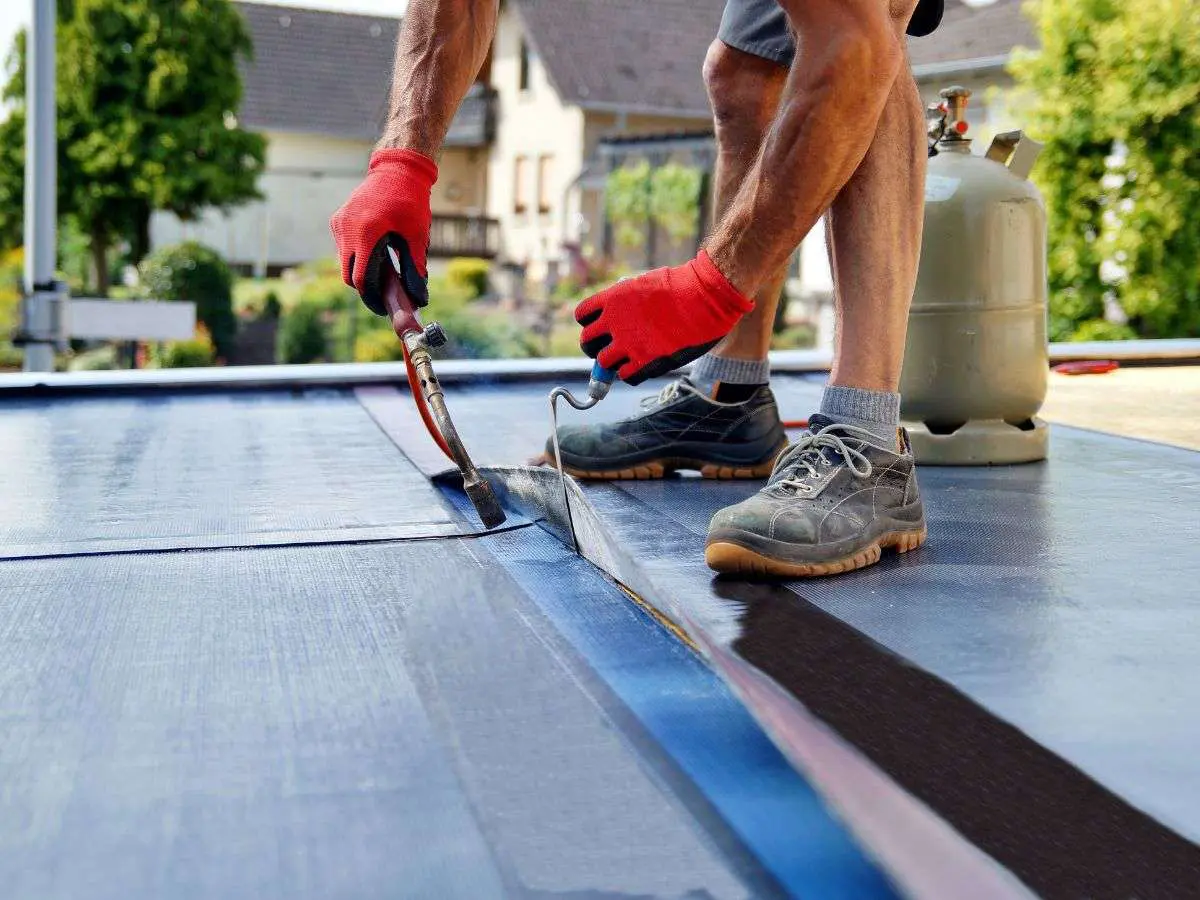

Flat roofs often require occasional repairs. Here are the most common ones:
Leak repair: Leaks are the most frequent issue with flat roofs. Water penetration can cause serious problems, including mold and structural damage. Fixing leaks quickly is essential to prevent further issues.
Patching and sealing: Cracks or holes in the roofing material can develop over time due to weather and wear. Patching these areas prevents water damage and extends the roof’s lifespan.
Recoating: Applying a new protective coating over the roof adds a waterproof barrier and improves durability. Recoating every few years helps maintain the roof and extends its life.
Gutter cleaning: Flat roofs often have gutters to direct water away. Clogged gutters can cause water pooling and damage. Regular cleaning ensures proper drainage and protects your roof.
Flat Roof Replacement Process
Replacing a flat roof involves several key steps:
- Inspection: Evaluate the roof to decide if repair or replacement is needed.
- Removing Old Material: If replacing, remove old shingles or roofing material.
- Repairing Damage: Fix any issues with the roof deck, like loose boards or damaged plywood.
- Installing Underlayment: Add a moisture-protecting underlayment before the new roof material.
- Choosing a Roof Type: Select materials like rubber membrane, metal, or modified bitumen based on budget and climate.
Installation: Proper installation by a professional roof installer ensures durability and code compliance.
Need Help With Your Flat Roof?
If you’re considering a flat roof, weigh the pros and cons before deciding. For repairs or a new roof, book a FREE Roof Inspection today. We’re expert roofing contractors in flat roofing and ready to assist with your roofing project!